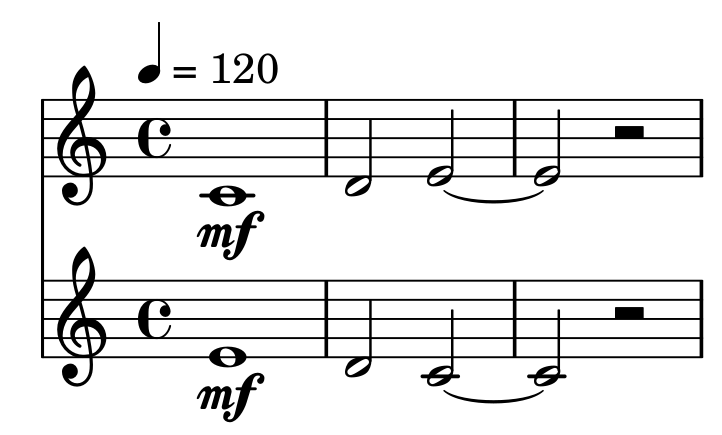Quick start¶
This is a very concise overview how to start fundamental mutwo operations.
Install all needed packages¶
pip3 install mutwo.core mutwo.music mutwo.midi mutwo.abjad
To render musical notation, install Lilypond.
Define tones, chords, rests¶
Tones, chords and rests can all be represented by using NoteLike:
from mutwo import music_events
tone = music_events.NoteLike('cs2', 2, 'f')
chord = music_events.NoteLike('c3 e3 g3', 1, 'pp')
rest = music_events.NoteLike([], 1)
Define a melody and a polyphony¶
from mutwo import core_events
from mutwo import music_events
melody = core_events.Consecution(
[music_events.NoteLike('c', 1), music_events.NoteLike('d', 0.5), music_events.NoteLike('e', 1)]
)
reversed_melody = melody.copy()
reversed_melody.reverse()
polyphony = core_events.Concurrence([melody, reversed_melody])
Export the polyphony to a MIDI file¶
from mutwo import midi_converters
e2m = midi_converters.EventToMidiFile()
e2m.convert(polyphony, 'polyphony.mid')
(rendered with TiMidity++)
Import a MIDI file¶
from mutwo import midi_converters
m2e = midi_converters.MidiFileToEvent()
event = m2e.convert('polyphony.mid')
Export the polyphony to a musical notation¶
Mutwo uses Abjad as an intermediate agent between itself and Lilypond:
from mutwo import abjad_converters
import abjad
ac = abjad_converters.ConsecutionToAbjadVoice()
s0 = abjad.Staff([ac.convert(polyphony[0])])
s1 = abjad.Staff([ac.convert(polyphony[1])])
score = abjad.Score([s0, s1])
lilypond_file = abjad.LilyPondFile()
lilypond_file.items.append(score)
abjad.persist.as_pdf(lilypond_file, 'polyphony.pdf')